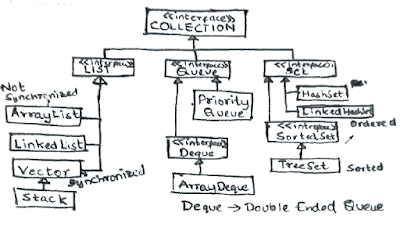
Java Collections Interview Questions
- Why do we need Collections in Java?
- What are the important methods that are declared in the Collection Interface?
- Can you explain briefly about the List Interface?
- Can you briefly explain about the Map Interface?
- What is the difference between Set and SortedSet?
- What is difference between Map and SortedMap?
- Explain briefly about Queue Interface?
- Explain briefly about Iterator?
- Explain about ArrayList with an example?
- Can an ArrayList have Duplicate elements?
- How do you iterate around an ArrayList using Iterator?
- How do you sort an ArrayList?
- How do you sort elements in an ArrayList using Comparable interface?
- How do you sort elements in an ArrayList using Comparator interface?
- How do you convert List to Array?
- How do you convert an Array to List?
- What is Vector class? How is it different from an ArrayList?
- What is LinkedList? What interfaces does it implement? How is it different from an ArrayList?
- Can you give examples of classes that implement the Set Interface?
- What is a HashSet?
- What is a LinkedHashSet? How is different from a HashSet?
- What is a TreeSet? How is different from a HashSet?
- Can you give examples of implementations of NavigableSet?
- What are the important methods in the NavigableSet interface?
- What are the different implementations of a Map Interface?
- What is a HashMap?
- What are the different methods in a Hash Map?
- What is a TreeMap? How is different from a HashMap?
- Can you give an example of implementation of NavigableMap Interface?
- What is a PriorityQueue?
- What are the static methods present in the Collections class?
- What is the difference between synchronized and concurrent collections in Java?
- Explain about the new concurrent collections in Java?
- Explain about CopyOnWrite concurrent collections approach?
- What is CompareAndSwap approach?
- What is a Lock? How is it different from using synchronized approach?
- What is initial capacity of a Java Collection?
- What is load factor of a HashMap?
- When does a Java collection throw UnsupportedOperationException?
- What is difference between fail-safe and fail-fast iterators?
- Explain about streams with an example?
- What are atomic operations in Java?
- What is BlockedQueue in Java?
Why do we need Collections in Java?
Arrays are not dynamic. Once an array of a particular size is declared, the size cannot be modified. To add a new element to the array, a new array has to be created with bigger size and all the elements from the old array copied to new array.
Collections are used in situations where data is dynamic. Collections allow adding an element, deleting an element and host of other operations. There are a number of Collections in Java allowing to choose the right Collection for the right context.
What are the important methods that are declared in the Collection Interface?
Most important methods declared in the collection interface are the methods to add and remove an element. add method allows adding an element to a collection and delete method allows deleting an element from a collection.
size() methods returns number of elements in the collection. Other important methods defined as part of collection interface are shown below.
interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>
{
boolean add(E paramE);
boolean remove(Object paramObject);
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
void clear();
boolean contains(Object paramObject);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> paramCollection);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> paramCollection);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> paramCollection);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> paramCollection);
Iterator<E> iterator();
//A NUMBER OF OTHER METHODS AS WELL..
}
Can you explain briefly about the List Interface?
List interface extends Collection interface. So, it contains all methods defined in the Collection interface. In addition, List interface allows operation specifying the position of the element in the Collection.
Most important thing to remember about a List interface - any implementation of the List interface would maintain the insertion order. When an element A is inserted into a List (without specifying position) and then another element B is inserted, A is stored before B in the List.
When a new element is inserted without specifying a position, it is inserted at the end of the list of elements.
However, We can also use the void add(int position, E paramE); method to insert an element at a specific position.
Listed below are some of the important methods in the List interface (other than those inherited from Collection interface):
interface List<E> extends Collection<E>
{
boolean addAll(int paramInt, Collection<? extends E> paramCollection);
E get(int paramInt);
E set(int paramInt, E paramE);
void add(int paramInt, E paramE);
E remove(int paramInt);
int indexOf(Object paramObject);
int lastIndexOf(Object paramObject);
ListIterator<E> listIterator();
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int paramInt);
List<E> subList(int paramInt1, int paramInt2);
}
Can you briefly explain about the Map Interface?
First and foremost, Map interface does not extend Collection interface. So, it does not inherit any of the methods from the Collection interface.
A Map interface supports Collections that use a key value pair. A key-value pair is a set of linked data items: a key, which is a unique identifier for some item of data, and the value, which is either the data or a pointer to the data. Key-value pairs are used in lookup tables, hash tables and configuration files. A key value pair in a Map interface is called an Entry.
Put method allows to add a key, value pair to the Map.
V put(K paramK, V paramV);
Get method allows to get a value from the Map based on the key.
V get(Object paramObject);
Other important methods in Map Inteface are shown below:
interface Map<K, V>
{
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean containsKey(Object paramObject);
boolean containsValue(Object paramObject);
V get(Object paramObject);
V put(K paramK, V paramV);
V remove(Object paramObject);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> paramMap);
void clear();
Set<K> keySet();
Collection<V> values();
Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
boolean equals(Object paramObject);
int hashCode();
public static abstract interface Entry<K, V>
{
K getKey();
V getValue();
V setValue(V paramV);
boolean equals(Object paramObject);
int hashCode();
}
}
What is the difference between Set and SortedSet?
SortedSet Interface extends the Set Interface. Both Set and SortedSet do not allow duplicate elements.
Main difference between Set and SortedSet is - an implementation of SortedSet interface maintains its elements in a sorted order. Set interface does not guarantee any Order. For example, If elements 4,5,3 are inserted into an implementation of Set interface, it might store the elements in any order. However, if we use SortedSet, the elements are sorted. The SortedSet implementation would give an output 3,4,5.
Important Operations in the SortedSet interface which are not present in the Set Interface are listed below:
public interface SortedSet<E> extends Set<E> {
SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement);
SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement);
SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement);
E first();
E last();
Comparator<? super E> comparator();
}
What is difference between Map and SortedMap?
SortedMap interface extends the Map interface. In addition, an implementation of SortedMap interface maintains keys in a sorted order.
Methods are available in the interface to get a ranges of values based on their keys.
public interface SortedMap<K, V> extends Map<K, V> {
Comparator<? super K> comparator();
SortedMap<K, V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey);
SortedMap<K, V> headMap(K toKey);
SortedMap<K, V> tailMap(K fromKey);
K firstKey();
K lastKey();
}
Explain briefly about Queue Interface?
STYLE : NoSpacing
Queue Interface extends Collection interface. Queue Interface is typically used for implementation holding elements in order for some processing.
STYLE : NoSpacing
Queue interface offers methods peek() and poll() which get the element at head of the queue. The difference is that poll() method removes the head from queue also. peek() would keep head of the queue unchanged.
interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E>
{
boolean offer(E paramE);
E remove();
E poll();
E element();
E peek();
}
Explain briefly about Iterator?
Iterator interface enables us to iterate (loop around) a collection. All collections define a method iterator() that gets an iterator of the collection.
hasNext() checks if there is another element in the collection being iterated. next() gets the next element.
public interface Iterator<E> {
boolean hasNext();
E next();
}
Explain about ArrayList with an example?
ArrayList implements the list interface. So, ArrayList stores the elements in insertion order (by default). Element’s can be inserted into and removed from ArrayList based on their position.
Let’s look at how to instantiate an ArrayList of integers.
List<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Code like below is permitted because of auto boxing. 5 is auto boxed into Integer object and stored in ArrayList.Add method (by default) adds the element at the end of the list.
integers.add(5);//new Integer(5)
Can an ArrayList have Duplicate elements?
ArrayList can have duplicates (since List can have duplicates).
List<String> arraylist = new ArrayList<String>();
//adds at the end of list
arraylist.add("Sachin");//[Sachin]
//adds at the end of list
arraylist.add("Dravid");//[Sachin, Dravid]
//adds at the index 0
arraylist.add(0, "Ganguly");//[Ganguly, Sachin, Dravid]
//List allows duplicates - Sachin is present in the list twice
arraylist.add("Sachin");//[ Ganguly, Sachin, Dravid, Sachin]
System.out.println(arraylist.size());//4
System.out.println(arraylist.contains("Dravid"));//true
How do you iterate around an ArrayList using Iterator?
Example below shows how to iterate around an ArrayList.
Iterator<String> arraylistIterator = arraylist
.iterator();
while (arraylistIterator.hasNext()) {
String str = arraylistIterator.next();
System.out.println(str);//Prints the 4 names in the list on separate lines.
}
How do you sort an ArrayList?
Example below shows how to sort an ArrayList. It uses the Collections.sort method.
List<String> numbers = new ArrayList<String>();
numbers.add("one");
numbers.add("two");
numbers.add("three");
numbers.add("four");
System.out.println(numbers);//[one, two, three, four]
//Strings - By Default - are sorted alphabetically
Collections.sort(numbers);
System.out.println(numbers);//[four, one, three, two]
How do you sort elements in an ArrayList using Comparable interface?
Consider the following class Cricketer.
class Cricketer implements Comparable<Cricketer> {
int runs;
String name;
public Cricketer(String name, int runs) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.runs = runs;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + " " + runs;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Cricketer that) {
if (this.runs > that.runs) {
return 1;
}
if (this.runs < that.runs) {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
}
Let’s now try to sort a list containing objects of Cricketer class.
List<Cricketer> cricketers = new ArrayList<Cricketer>();
cricketers.add(new Cricketer("Bradman", 9996));
cricketers.add(new Cricketer("Sachin", 14000));
cricketers.add(new Cricketer("Dravid", 12000));
cricketers.add(new Cricketer("Ponting", 11000));
System.out.println(cricketers);
//[Bradman 9996, Sachin 14000, Dravid 12000, Ponting 11000]
Now let’s try to sort the cricketers.
Collections.sort(cricketers); System.out.println(cricketers); //[Bradman 9996, Ponting 11000, Dravid 12000, Sachin 14000]
How do you sort elements in an ArrayList using Comparator interface?
Other option to sort collections is by creating a separate class which implements Comparator interface.
Example below:
class DescendingSorter implements Comparator<Cricketer> {
//compareTo returns -1 if cricketer1 < cricketer2
// 1 if cricketer1 > cricketer2
// 0 if cricketer1 = cricketer2
//Since we want to sort in descending order,
//we should return -1 when runs are more
@Override
public int compare(Cricketer cricketer1,
Cricketer cricketer2) {
if (cricketer1.runs > cricketer2.runs) {
return -1;
}
if (cricketer1.runs < cricketer2.runs) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
}
Let’s now try to sort the previous defined collection:
Collections
.sort(cricketers, new DescendingSorter());
System.out.println(cricketers);
//[Sachin 14000, Dravid 12000, Ponting 11000, Bradman 9996]
How do you convert List to Array?
There are two ways. First is to use toArray(String) function. Example below. This creates an array of String's
List<String> numbers1 = new ArrayList<String>();
numbers1.add("one");
numbers1.add("two");
numbers1.add("three");
numbers1.add("four");
String[] numbers1Array = new String[numbers1.size()];
numbers1Array = numbers1.toArray(numbers1Array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers1Array));
//prints [one, two, three, four]
Other option is to use toArray() function. Example below. This creates an array of Objects.
Object[] numbers1ObjArray = numbers1.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays
.toString(numbers1ObjArray));
//[one, two, three, four]
How do you convert an Array to List?
We can use the Arrays.asList method.
String values[] = { "value1", "value2", "value3" };
List<String> valuesList = Arrays.asList(values);
System.out.println(valuesList);//[value1, value2, value3]
What is Vector class? How is it different from an ArrayList?
Vector has the same operations as an ArrayList. However, all methods in Vector are synchronized. So, we can use Vector if we share a list between two threads and we would want to them synchronized.
What is LinkedList? What interfaces does it implement? How is it different from an ArrayList?
Linked List extends List and Queue.Other than operations exposed by the Queue interface, LinkedList has the same operations as an ArrayList. However, the underlying implementation of Linked List is different from that of an ArrayList.
ArrayList uses an Array kind of structure to store elements. So, inserting and deleting from an ArrayList are expensive operations. However, search of an ArrayList is faster than LinkedList.
LinkedList uses a linked representation. Each object holds a link to the next element. Hence, insertion and deletion are faster than ArrayList. But searching is slower.
Can you give examples of classes that implement the Set Interface?
HashSet, LinkedHashSet and TreeSet implement the Set interface. These classes are described in great detail in the video - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W5c8uXi4qTw
What is a HashSet?
HashSet implements set interface. So, HashSet does not allow duplicates. However, HashSet does not support ordering. The order in which elements are inserted is not maintained.
HashSet Example
Set<String> hashset = new HashSet<String>();
hashset.add("Sachin");
System.out.println(hashset);//[Sachin]
hashset.add("Dravid");
System.out.println(hashset);//[Sachin, Dravid]
Let’s try to add Sachin to the Set now. Sachin is Duplicate. So will not be added. returns false.
hashset.add("Sachin");//returns false since element is not added
System.out.println(hashset);//[Sachin, Dravid]
What is a LinkedHashSet? How is different from a HashSet?
LinkedHashSet implements set interface and exposes similar operations to a HashSet. Difference is that LinkedHashSet maintains insertion order. When we iterate a LinkedHashSet, we would get the elements back in the order in which they were inserted.
What is a TreeSet? How is different from a HashSet?
TreeSet implements Set, SortedSet and NavigableSet interfaces.TreeSet is similar to HashSet except that it stores element’s in Sorted Order.
Set<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<String>();
treeSet.add("Sachin");
System.out.println(treeSet);//[Sachin]
Notice that the list is sorted after inserting Dravid.
//Alphabetical order
treeSet.add("Dravid");
System.out.println(treeSet);//[Dravid, Sachin]
Notice that the list is sorted after inserting Ganguly.
treeSet.add("Ganguly");
System.out.println(treeSet);//[Dravid, Ganguly, Sachin]
Sachin is Duplicate. So will not be added. returns false.
treeSet.add("Sachin");//returns false since element is not added
System.out.println(treeSet);//[Dravid, Ganguly, Sachin]
Can you give examples of implementations of NavigableSet?
TreeSet implements this interface. Let's look at an example with TreeSet. Note that elements in TreeSet are sorted.
TreeSet<Integer> numbersTreeSet = new TreeSet<Integer>(); numbersTreeSet.add(55); numbersTreeSet.add(25); numbersTreeSet.add(35); numbersTreeSet.add(5); numbersTreeSet.add(45);
What are the important methods in the NavigableSet interface?
NavigableSet interface has following methods.
Lower method finds the highest element lower than specified element. Floor method finds the highest element lower than or equal to specified element. Corresponding methods for finding lowest number higher than specified element are higher and ceiling.
//Find the highest number which is lower than 25 System.out.println(numbersTreeSet.lower(25));//5 //Find the highest number which is lower than or equal to 25 System.out.println(numbersTreeSet.floor(25));//25 //Find the lowest number higher than 25 System.out.println(numbersTreeSet.higher(25));//35 //Find the lowest number higher than or equal to 25 System.out.println(numbersTreeSet.ceiling(25));//25
What are the different implementations of a Map Interface?
HashMap and TreeMap. These classes are explained in detail in this video - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZNhT_Z8_q9s.
What is a HashMap?
HashMap implements Map interface – there by supporting key value pairs. Let’s look at an example.
HashMap Example
Map<String, Cricketer> hashmap = new HashMap<String, Cricketer>();
hashmap.put("sachin",
new Cricketer("Sachin", 14000));
hashmap.put("dravid",
new Cricketer("Dravid", 12000));
hashmap.put("ponting", new Cricketer("Ponting",
11500));
hashmap.put("bradman", new Cricketer("Bradman",
9996));
What are the different methods in a Hash Map?
get method gets the value of the matching key.
System.out.println(hashmap.get("ponting"));//Ponting 11500
//if key is not found, returns null.
System.out.println(hashmap.get("lara"));//null
If existing key is reused, it would replace existing value with the new value passed in.
//In the example below, an entry with key "ponting" is already present.
//Runs are updated to 11800.
hashmap.put("ponting", new Cricketer("Ponting",
11800));
//gets the recently updated value
System.out.println(hashmap.get("ponting"));//Ponting 11800
What is a TreeMap? How is different from a HashMap?
TreeMap is similar to HashMap except that it stores keys in sorted order. It implements NavigableMap interface and SortedMap interfaces along with the Map interface.
Map<String, Cricketer> treemap = new TreeMap<String, Cricketer>();
treemap.put("sachin",
new Cricketer("Sachin", 14000));
System.out.println(treemap);
//{sachin=Sachin 14000}
We will now insert a Cricketer with key dravid. In sorted order,dravid comes before sachin. So, the value with key dravid is inserted at the start of the Map.
treemap.put("dravid",
new Cricketer("Dravid", 12000));
System.out.println(treemap);
//{dravid=Dravid 12000, sachin=Sachin 14000}
We will now insert a Cricketer with key ponting. In sorted order, ponting fits in between dravid and sachin.
treemap.put("ponting", new Cricketer("Ponting",
11500));
System.out.println(treemap);
//{dravid=Dravid 12000, ponting=Ponting 11500, sachin=Sachin 14000}
treemap.put("bradman", new Cricketer("Bradman",
9996));
System.out.println(treemap);
//{bradman=Bradman 9996, dravid=Dravid 12000, ponting=Ponting 11500, sachin=Sachin 14000}
Can you give an example of implementation of NavigableMap Interface?
TreeMap is a good example of a NavigableMap interface implementation. Note that keys in TreeMap are sorted.
TreeMap<Integer, Cricketer> numbersTreeMap = new TreeMap<Integer, Cricketer>();
numbersTreeMap.put(55, new Cricketer("Sachin",
14000));
numbersTreeMap.put(25, new Cricketer("Dravid",
12000));
numbersTreeMap.put(35, new Cricketer("Ponting",
12000));
numbersTreeMap.put(5,
new Cricketer("Bradman", 9996));
numbersTreeMap
.put(45, new Cricketer("Lara", 10000));
lowerKey method finds the highest key lower than specified key. floorKey method finds the highest key lower than or equal to specified key. Corresponding methods for finding lowest key higher than specified key are higher and ceiling. A few examples using the Map created earlier below.
//Find the highest key which is lower than 25 System.out.println(numbersTreeMap.lowerKey(25));//5 //Find the highest key which is lower than or equal to 25 System.out.println(numbersTreeMap.floorKey(25));//25 //Find the lowest key higher than 25 System.out.println(numbersTreeMap.higherKey(25));//35 //Find the lowest key higher than or equal to 25 System.out.println(numbersTreeMap.ceilingKey(25));//25
What is a PriorityQueue?
PriorityQueue implements the Queue interface.
//Using default constructor - uses natural ordering of numbers //Smaller numbers have higher priority PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
Adding an element into priority queue - offer method
priorityQueue.offer(24); priorityQueue.offer(15); priorityQueue.offer(9); priorityQueue.offer(45); System.out.println(priorityQueue);//[9, 24, 15, 45]
Peek method examples
//peek method get the element with highest priority.
System.out.println(priorityQueue.peek());//9
//peek method does not change the queue
System.out.println(priorityQueue);//[9, 24, 15, 45]
//poll method gets the element with highest priority.
System.out.println(priorityQueue.poll());//9
//peek method removes the highest priority element from the queue.
System.out.println(priorityQueue);//[24, 15, 45]
//This comparator gives high priority to the biggest number.
Comparator reverseComparator = new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer paramT1,
Integer paramT2) {
return paramT2 - paramT1;
}
};
What are the static methods present in the Collections class?
- static int binarySearch(List, key)
- Can be used only on sorted list
- static int binarySearch(List, key, Comparator)
- static void reverse(List)
- Reverse the order of elements in a List.
- static Comparator reverseOrder();
- Return a Comparator that sorts the reverse of the collection current sort sequence.
- static void sort(List)
- static void sort(List, Comparator)
What is the difference between synchronized and concurrent collections in Java?
Synchronized collections are implemented using synchronized methods and synchronized blocks. Only one thread can executing any of the synchronized code at a given point in time. This places severe restrictions on the concurrency of threads – thereby affecting performance of the application. All the pre Java 5 synchronized collections (HashTable & Vector, for example) use this approach.
Post Java 5, collections using new approaches to synchronization are available in Java. These are called concurrent collections. More details below.
Explain about the new concurrent collections in Java?
Post Java 5, collections using new approaches to synchronization are available in Java. These are called concurrent collections. Examples of new approaches are :
- Copy on Write
- Compare and Swap
- Locks
These new approaches to concurrency provide better performance in specific context’s. We would discuss each of these approaches in detail below.
Explain about CopyOnWrite concurrent collections approach?
Important points about Copy on Write approach
- All values in collection are stored in an internal immutable (not-changeable) array. A new array is created if there is any modification to the collection.
- Read operations are not synchronized. Only write operations are synchronized.
Copy on Write approach is used in scenarios where reads greatly out number write’s on a collection. CopyOnWriteArrayList & CopyOnWriteArraySet are implementations of this approach. Copy on Write collections are typically used in Subject – Observer scenarios, where the observers very rarely change. Most frequent operations would be iterating around the observers and notifying them.
What is CompareAndSwap approach?
Compare and Swap is one of the new approaches (Java 5) introduced in java to handle synchronization. In traditional approach, a method which modifies a member variable used by multiple threads is completely synchronized – to prevent other threads accessing stale value.
In compare and swap approach, instead of synchronizing entire method, the value of the member variable before calculation is cached. After the calculation, the cached value is compared with the current value of member variable. If the value is not modified, the calculated result is stored into the member variable. If another thread has modified the value, then the calculation can be performed again. Or skipped – as the need might be.
ConcurrentLinkedQueue uses this approach.
What is a Lock? How is it different from using synchronized approach?
When 10 methods are declared as synchronized, only one of them is executed by any of the threads at any point in time. This has severe performance impact.
Another new approach introduced in Java 5 is to use lock and unlock methods. Lock and unlock methods are used to divide methods into different blocks and help enhance concurrency. The 10 methods can be divided into different blocks, which can be synchronized based on different variables.
What is initial capacity of a Java Collection?
Extract from the reference : http://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/util/HashMap.html. An instance of HashMap has two parameters that affect its performance: initial capacity and load factor. The capacity is the number of buckets in the hash table, and the initial capacity is simply the capacity at the time the hash table is created. The load factor is a measure of how full the hash table is allowed to get before its capacity is automatically increased. When the number of entries in the hash table exceeds the product of the load factor and the current capacity, the hash table is rehashed (that is, internal data structures are rebuilt) so that the hash table has approximately twice the number of buckets.
As a general rule, the default load factor (.75) offers a good tradeoff between time and space costs. Higher values decrease the space overhead but increase the lookup cost (reflected in most of the operations of the HashMap class, including get and put).
The expected number of entries in the map and its load factor should be taken into account when setting its initial capacity, so as to minimize the number of rehash operations.
What is load factor?
Refer answer to Initial Capacity above.
When does a Java collection throw UnsupportedOperationException?
All Java Collections extend Collection interface. So, they have to implement all the methods in the Collection interface. However, certain Java collections are optimized to be used in specific conditions and do not support all the Collection operations (methods). When an unsupported operation is called on a Collection, the Collection Implementation would throw an UnsupportedOperationException.
Arrays.asList returns a fixed-size list backed by the specified array. When an attempt is made to add or remove from this collection an UnsupportedOperationException is thrown. Below code throws UnsupportedOperationException.
List<String> list=Arrays.asList(new String[]{"ac","bddefe"});
list.remove();//throws UnsupportedOperationException
What is difference between fail-safe and fail-fast iterators?
Fail Fast Iterators throw a ConcurrentModificationException if there is a modification to the underlying collection is modified. This was the default behavior of the synchronized collections of pre Java 5 age.
Fail Safe Iterators do not throw exceptions even when there are changes in the collection. This is the default behavior of the concurrent collections, introduced since Java 5.
Explain about streams with an example?
Streams are introduced in Java 8. In combination with Lambda expressions, they attempt to bring some of the important functional programming concepts to Java.
A stream is a sequence of elements supporting sequential and parallel aggregate operations. Consider the example code below. Following steps are done:
- Step I : Creating an array as a stream
- Step II : Use Lambda Expression to create a filter
- Step III : Use map function to invoke a String function
- Step IV : Use sorted function to sort the array
- Step V : Print the array using forEach
Arrays.stream(new String[] {
"Ram", "Robert", "Rahim"
})
.filter(s - > s.startsWith("Ro"))
.map(String::toLowerCase)
.sorted()
.forEach(System.out::println);
In general any use of streams involves
- Source - Creation or use of existing stream : Step I above
- Intermediate Operations - Step II, III and IV above. Intermediate Operations return a new stream
- Terminal Operation – Step V. Consume the stream. Print it to output or produce a result (sum,min,max etc).
Intermediate Operations are of two kinds
- Stateful : Elements need to be compared against one another (sort, distinct etc)
- Stateless : No need for comparing with other elements (map, filter etc)
What are atomic operations in Java?
Atomic Access Java Tutorial states “In programming, an atomic action is one that effectively happens all at once. An atomic action cannot stop in the middle: it either happens completely, or it doesn't happen at all. No side effects of an atomic action are visible until the action is complete”.
Let’s assume we are writing a multi threaded program. Let’s create an int variable i. Even a small operation, like i++ (increment), is not thread safe. i++ operation involves three steps.
- Read the value which is currently stored in i
- Add one to it (atomic operation).
- Store it in i
In a multi-threaded environment, there can be unexpected results. For example, if thread1 is reading the value (step 1) and immediately after thread2 stores the value (step 3).
To prevent these, Java provides atomic operations. Atomic operations are performed as a single unit without interference from other threads ensuring data consistency.
A good example is AtomicInteger. To increment a value of AtomicInteger, we use the incrementAndGet() method. Java ensures this operation is Atomic.
What is BlockedQueue in Java?
BlockedQueue interface is introduced in Java specifically to address specific needs of some Producer Consumer scenarios. BlockedQueue allows the consumer to wait (for a specified time or infinitely) for an element to become available.
If you loved these Questions, you will love our PDF Interview Guide with 400+ Questions.
Download it now!.
- Java : Core Java, Advanced Java, Generics, Exception Handling, Serialization, Threads, Synchronization, Java New Features
- Frameworks : Spring, Spring MVC, Struts, Hibernate
- Design : Design, Design Patterns, Code Review
- Architecture : Architecture, Performance & Load Testing, Web Services, REST Web Services,Security, Continuous Integration